Using Analytic Hierarchy Process to Determine Optimal Locations for Fire Observation Towers in Iran’s Shafarood Forest
Summary
Forests have been seriously affected by fire; therefore, it is necessary to detect fire from the observation towers. Currently, the number of observation towers and the effectiveness of their distribution is unknown. The aim of the current research is to determine the current and potential areas that can be seen from the observation towers. Another goal of this research is to propose a new network to maximize its effectiveness. The analysis of the field of view in ArcGIS software was done by integrating the digital height model and the road network map, vegetation cover, etc. to determine the entire surface of a field of view. It was found that the observation towers resulting from the designed model approximately cover the studied area for the supervision of the security staff. In addition to the designed model, an experienced expert staff took a close look at the field with GPS and according to the experiences, selected places for the construction of an observation tower and placed them on the designed model, and then witnessed the approximate coverage of the field visit. We have been with the model.
Keywords: Fuzzy gamma model, AHP, field of view analysis, observation towers, forest fire, model
Introduction
Appropriate design of routes and optimal planning of forest roads are effective factors in the sustainable development of forests, which increase the efficiency of the road network, reduce costs, and prevent forest destruction. A proper network of forest roads, in addition to transporting goods and forest products, can assist maintenance and support services, provide access to the forest depths, improve village communication, and support tourism and protection activities. In forest areas, the proper design of the observation stations can reduce damage caused to the forest, and at the same time the space for its optimal management can be provided. The topographic map and its implementation in the field is the main infrastructure of forest project preparation, which is considered the most important and most difficult part of it. It requires extensive high-level expertise because it will be very unlikely and even impossible to compensate for possible mistakes in this part.
In a study of observation stations based on the principles for the construction of an environmental road using GIS, taking into account the influencing factors including geology, soil erodibility, slope, land use, water flows, mud, and height, they evaluated the above factors and showed that the optimal route can be drawn by identifying the above-influencing factors. Some researchers used GIS identification to locate the route that has the least environmental effects on the surrounding environment. Creating observation stations with different goals in forest areas is one of the executive elements of scientific and optimal management in forest areas and away towards the sustainable development of forest populations. In addition to being expensive in design, construction, and maintenance, observation stations also have negative effects on the environment and animals. The animals have a special sensitivity from an economic point of view – the environment is a public concern. Therefore, proper design and compliance with the necessary standards will be necessary for this matter because the network of observation stations with the allocation of a large amount of capital is one of the most important cost factors in forest management. The efficiency of the network of stations can be increased. In order to achieve this goal, it is necessary to study the effective factors in the design of the network of observation stations in a region in order to choose the most suitable route.
The presented study was conducted with the aim of preparing a suitable possibility map for observation stations in Seri in combination with studies using GIS capability, observing the environmental principles and technical characteristics of the stations in order to provide suitable places for the construction of observation towers.
Materials and Methods
Before the implementation of the forest nationalization law of 1342, the private forests were in the hands of the land owners of the region and were mainly used for grazing livestock and providing wood needed by forest dwellers or for charcoal extraction. When natural resources were declared national in 1342, the government became the owner of all the forests and pastures of the country, and of course, the exploitation of these resources also came under the control of the government. Although after this year, the forest was given to the government as an Anfal in order to use its income for the development and settlement of the country, the illegal harvesting by forest dwellers, excessive grazing of livestock, and wood smuggling continues today.
In the forests of the north of the country, due to the high forest cover and the topic of forest wood smuggling, it is possible to monitor the forest with observation towers and the appointment of a guard in these towers along with a wireless connection. According to the mentioned cases, the construction of these towers in the forests of the north of the country requires an expert and trained group in order to be able to select a suitable place for the construction of these towers in the first stage and proceed with its construction in the next stage. The topic to be studied in this project is to find a suitable place to build observation towers in the forest.
Study Area
The studied area in Gilan province is under the supervision of the Razvanshahr governorate in terms of country divisions. Series 14 of Rosedale Pasht and Series 15 of Shirewa constitute the studied area and are considered to be part of the northern series from the point of view of geography. The total area of the two, according to the calculation made through GIS, is an estimated 3733.81 hectares. The geographical location, limits, and extent of the plan studied area are located at latitude 37° 31′ 40″ and 37° 30′ 05″ and longitude 48° 55′ 00″ and 49° 01′ 50″. The mentioned series is limited to the Khosabar river from the north, to the large ridge of Orma from the south, to the Baneh valley at the head of the Shafarud river from the east, and to the Siah Dol valley and the Khoshayr river from the west.
Location data used
The available maps are from the natural resource maps on the scale of 1:25000 of the Razvanshahr index, through which the desired criteria such as the study area, a survey of topographical effects and altitude and elevation, and network of forest roads were extracted. The DEM elevation model was used to draw elevation and slope maps, as well as aerial photographs with dimensions of 23×23 cm with a scale of 1:20000 of the mapping organization were used to plan field operations and select the area.
Method
Examining the influencing factors in the location of the watch tower, and identifying and selecting the factors that influence the location, is one of the important stages of the study. The more identified factors are more consistent with the ground reality, the more positioning results will be more satisfactory.
Affecting Factors
After identifying the effective factors in the studied series, a map of each of the above factors was prepared according to the purpose of the study. The prepared maps, including the series slope map corresponding to the required slope classes in the north of the country, the elevation map and the road network map were converted into a raster structure for spatial analysis.
Classification of classes of maps of influential factors
For each of the influential factors in creating the possibility map, a raster format map was prepared. Each of the maps has several layers. which were arranged in categories from 1 to 5 according to their influence and role. The classes that have a higher ability to build towers were assigned the 1st rank, and the rest of the classes were assigned the next rank in the above range.
Valuing influential factors in map preparation
As it was said, a classified map was prepared for each of the influential factors in creating the watch tower. Of course, the role of these factors in creating the watch tower map is the same and therefore the above factors were weighted. The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) method, which is one of the efficient methods in multi-criteria decision-making, was used.
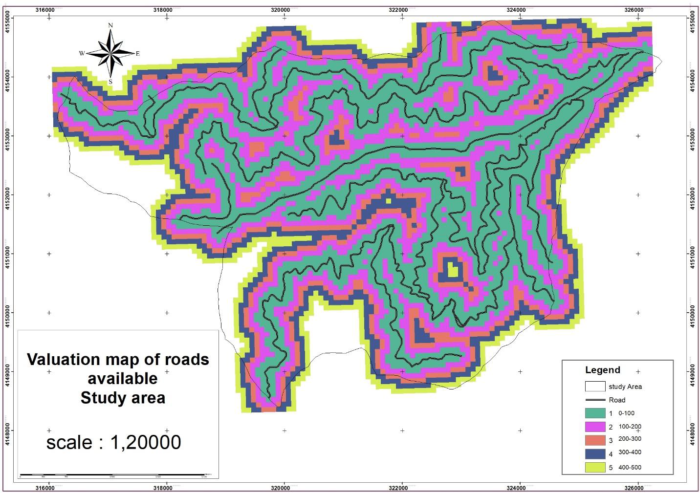
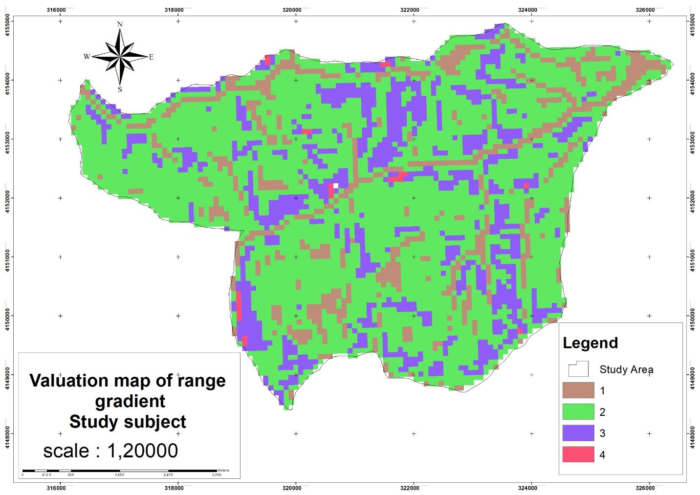
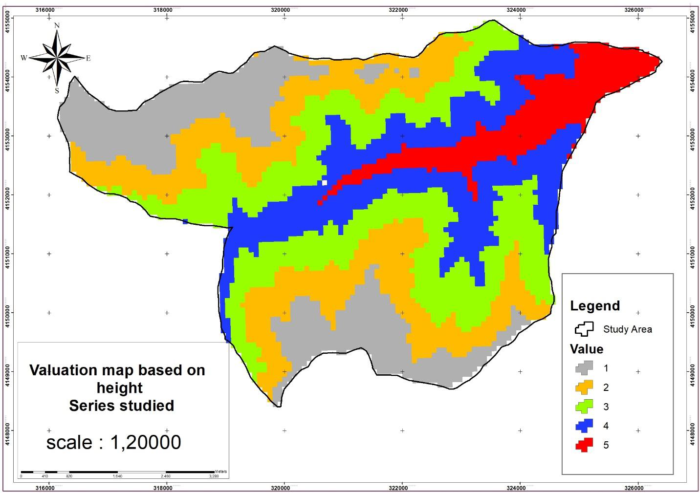
Considering that the roads are one of the important accessible factors in the forest in the construction of the towers, we should pay attention to this item and prioritize the places that are closer to the road. As a result, the areas that were closer to the road have given a value of 1 (Figure 1). Also, the slope factor in the forest is a limiting factor, as a result, high slopes are not suitable for building towers (Figure 2). In the elevation map for the construction of towers, the higher the height, the better the visibility will be, so the higher the height is the priority (Figure 3).
Results and suggestions
The weighted pairwise comparison method is part of the AHP method, which was proposed by Saati in 1980, and is one of the effective techniques in multiple decision-making. In the weighting method of paired comparison, criteria are compared two by two and their importance is determined relative to each other. Then a matrix is created whose input is the determined weights and its output is the relative weights related to the criteria (Malszewski, 1999). Next, in order to integrate the weighted information layers in the above steps, each of these layers was compared with each other by the AHP method, and then their compatibility matrix was prepared and finally, the weight of each layer was determined. The construction should be located in the areas of the forest where the shortage is felt. For this purpose, using the maps of the General Department of Natural Resources, sensitive and suitable places were identified and the areas that had more value for the construction of the tower were assigned a weight of 1.
The effective factors were identified for road clearance, height, and slope according to their importance. Questionnaires were completed by the relevant experts two by two (Malczewski, 1999) and the results were analyzed using export choice software. Due to its high accuracy and simple application, it was used for weighting, which was the most comprehensive system designed for decision-making with multiple criteria, and it was possible to formulate the problem by considering different qualitative and quantitative criteria in a hierarchical manner. This process involves different options in decision-making and provides the possibility of sensitivity analysis on criteria and sub-criteria (Qodsipour, 2019). A comparison matrix was formed in this method and the factors were compared in pairs and their weights were calculated. This calculation was theoretical and the range of relative weight changes was between 1 and 9 (Table 1).
| Information Layers: | Height | Slope | Road |
| Weight: | 0.073 | 0.727 | 0.200 |
Preparation of a map of the possibility of building an observation tower
Finally, in order to prepare the final map of the location of the watchtowers of the Shafarood forests, the layers obtained by combining the layers were prepared using the AHP method in ArcMap. The relative weights determined in this step for different factors are relative to the corresponding raster maps given. The weighted maps of different factors were combined in the GIS environment and a possibility map was prepared. The value of each cell of this map indicated the higher relative power of that cell for construction. The mentioned map was re-classified into 5 regions (suitable, relatively suitable, relatively high-risk, high-risk, and very high-risk areas) (Figure 4).
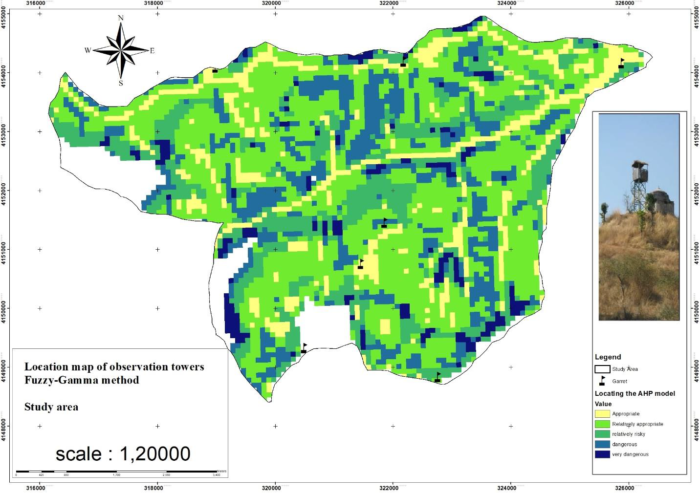
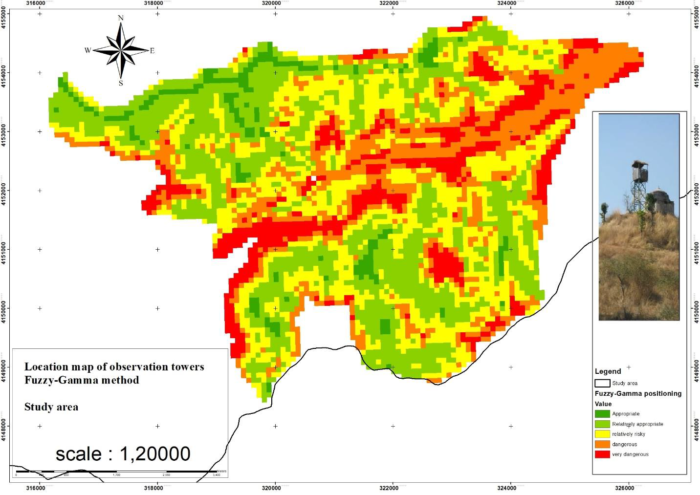
As shown in Figure 4, the range of Shafarood in terms of the location of watchtowers to 5 the class is classified that in areas with higher scores, the need to build these facilities is felt. In addition to the AHP model, you also used a fuzzy model. In the fuzzy gamma model, a coefficient of 0.9 is used, which is closer to AHP (Figure 5).
Results
According to the opinion of experts, seven observation towers are necessary for the study area.
The resulting raster maps combine the slope, height, and road, and are therefore very useful for planners, because it indicates where in this area, according to the probability of fire and the value of land and smuggling, more attention is needed.
In addition to the model prepared in GIS, a field visit was made to the study area with a group of relevant experts, and the areas that have the best location according to the mentioned factors were selected for the construction of a watch tower with GPS. Then, after transferring the collection points to ArcMap, it was observed that the model is consistent with the field visit and can cover the model. The forests of northern Iran are prone to destruction and indiscriminate cutting, and natural and human disturbances should be investigated in them and their effects should be investigated and a zoning map with the correct location can be reached.
In the continuation of this report, the fauna, soil, and climate factors of the region can be examined and we can reach a more complete map. Due to the limited time, I was able to finish the project here. With the map of risk zoning or location, we can achieve many achievements in the planning of the land.
